Einstein's Equation of Photoelectric Effect
Einstein's Equation of Photoelectric Effect: Overview
This topic consists of various concepts like Maximum Kinetic Energy of Photoelectrons,Variation of Photoelectric Current with Photon Intensity,Einstein's Equation of Photoelectric Effect, etc.
Important Questions on Einstein's Equation of Photoelectric Effect
The maximum kinetic energy of a photoelectron is . Its stopping potential is
The Einstein’s photoelectric equation is:
The Einstein’s photoelectric equation is:
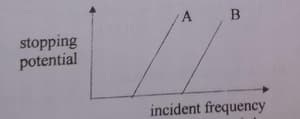
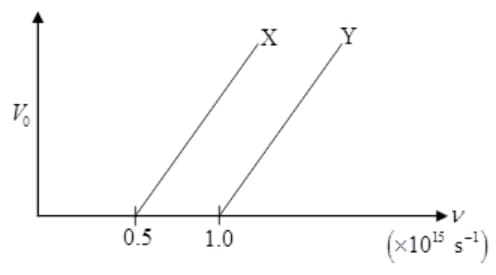
The following graph shows the variation of stopping potential with frequency of the incident radiation for two photosensitive metals and .
Which metal has
(i) a smaller threshold wavelength?
(ii) smaller kinetic energy?
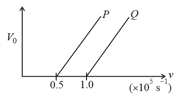
The following graph shows the variation of stopping potential with the frequency of the incident radiation for two photosensitive metals and :
(i) Which of the metals has larger threshold wavelength? Give reason.
(ii) Explain, giving reason, which metal gives out electrons, having larger kinetic energy, for the same wavelength of the incident radiation.
The graph between frequency of incident radiations and stopping potential for a given photosensitive material is as follows.
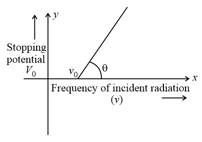
What information can be obtained from the value of the intercept on the potential axis?
The graph between frequency of incident radiations and stopping potential for a given photosensitive material is as follows.
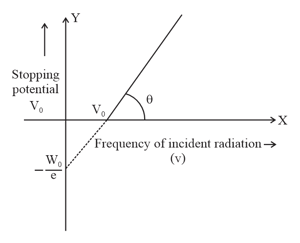
What information can be obtained from the value of the intercept on the potential axis?
Show graphically how the stopping potential for a given photosensitive surface varies with the frequency of the incident radiation.
In the photo-electron emission, the energy of the emitted electron is
The maximum kinetic energy of electrons emitted in the photoelectric effect is linearly dependent on the________________ of the incident radiation.
A copper ball of radius and work function is irradiated with ultraviolet radiation of wavelength . The effect of irradiation results in the emission of electrons from the ball. Further the ball will acquire charge and due to this there will be a finite value of the potential on the ball. The charge acquired by the ball is :
The cathode of a photocell (illuminated with monochromatic light) is coated with Caesium that has a work function of . When a voltage of is applied to the anode (w.r.t the cathode), it stops the flow of current in the circuit. The wavelength of the incident light is
A Hydrogen-like atom has atomic number . Photons emitted in the electronic transitions from level to level in these atoms are used to perform photoelectric effect experiment on a target metal. The maximum kinetic energy of the photoelectrons generated is . If the photoelectric threshold wavelength for the target metal is , the value of is _____.
[Given and , where is the Rydberg constant, is the Planck’s constant and is the speed of light in vacuum]
If a substance absorbs radiation of wavelength and emits radiation of wavelength , then the net change in energy is . Find the value of to the nearest integer.
Stopping potential of a metal when illuminated with light of wavelength is and that for wavelength is . The threshold wavelength of metal is
Find the
(a) maximum frequency
(b) minimum wavelength of X-rays produced byelectrons.
The stopping potential of a metal is , when it is illuminated by light of wavelength . What will be the stopping potential of the metal when the wavelength is ? (Photoelectric emission takes place in both the cases)
An LED is constructed from a p-n junction diode using . The energy gap is .The of light emitted will be equal to
The electric field associated with a monochromatic beam of light becomes zero, with frequency times per second. Find the maximum kinetic energy of the photoelectrons when this light falls on a metal surface whose work function is .
For a graph shown between stopping potential and incident frequency of radiation for two metal surfaces A and B. which metal needs a larger wavelength for the emission of photoelectron?